Below I have listed the different categories under which each entity operated on by the web crawler will fall.
- Genes
- Proteins
- Molecules (drugs)
- Transmitters (neurotransmitters, inflammatory cytokines etc.)
- Receptors
- Processes (e.g. apoptosis, glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation)
- Effect (upregulates, downregulates)
- ALS type (SOD1 mouse, healthy yeast, limb-onset SALS…)
- Laboratory anomalies (homocysteine ceruloplasmin, lipopolysaccharide)
From this initial data, the target is to distill something that can be used to
- estimate the relevance of a given molecule as part of an ALS therapeutic cocktail as widely as possible
- find pathways through which ALS could be subdivided into categories in order to enable separate therapeutics development for each category
Examples of entities in different categories
Proteins.
| ceruloplasmin | Appears to be low in PALS’ serum. Also present as an antioxidant in CNS. | |
| SOD1 | superoxide dismutase 1 | One of the clumping proteins in ALS. Possible inter-cellular spreading agent. |
| TDP-43 | tar DNA-binding protein 43 | Major clumping protein in SALS. |
| FUS | fused in sarcoma | Another clumping protein. |
| MMP-9 | matrix metalloproteinase 9 | Seems to correlate with cell’s vulnerability in ALS. |
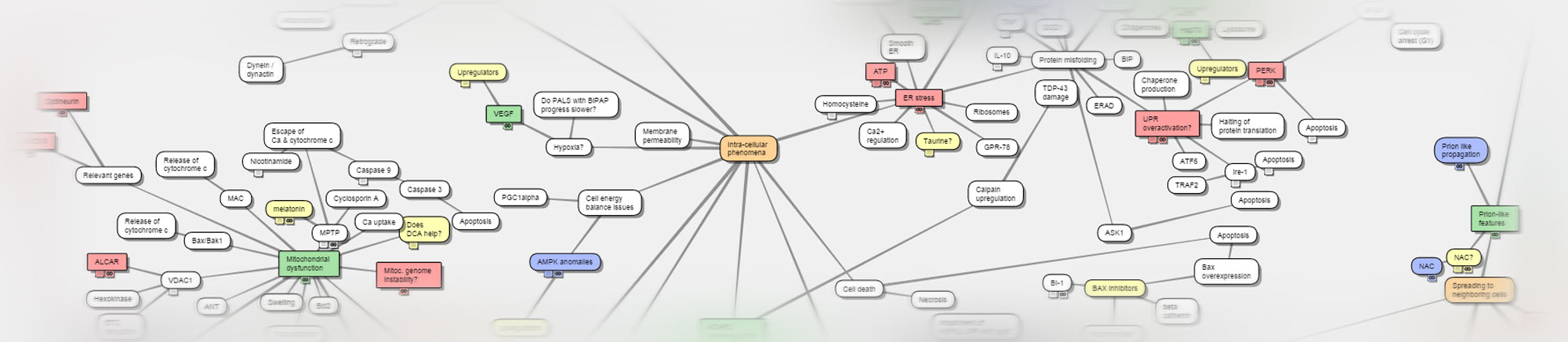
Processes.
| Astrocytosis | Occurs in ALS patients and presumably contributes to neuron destruction. | |
| Endocytosis | Probable route through which SOD1 enters neurons. | |
| Glycolysis | Possibly upregulated in ALS | |
| Oxidative phosphorylation | Possibly downregulated in ALS. | |
| Mitochondriopathy | One characteristic process in ALS | |
| Protein folding | Place where something seems to go wrong. | |
| Protein misfolding | Characteristic phenomenon in ALS. | |
| Protein aggregation | Protein clumping | Characteristic phenomenon in ALS. |
| Axonal transport | Another place where things seem to go awry. | |
| Apoptosis | Assumed mechanism of neuron destruction. | |
| Neuroinflammation | Another potentiall mechanism for neuron destruction. | |
| UPR activation | Presumed to occur | |
| Stress granule formation | Takes place in affected neurons | |
| ADAR2 downregulation | Present at least in some ALS forms | |
| Protein recycling failures | Typically present in affected neurones | |
| Dysregulation of cytosolic calcium | Typically present in affected neurones | |
| ER stress | Endoplasmic reticulum stress | Typically present in affected neurones |
| Oxidative stress | One of the most prominent ALS processes | |
| Hepatic steatosis | Apparently present in majority of PALS. | |
| BBB leakage | leaking blood brain barrier | Occurs early on in disease progression. |
Transmitters.
| Glutamate | Assumed source of neurotoxicity | |
| GABA | Counters the glutamate-induced excitation. | |
| Nerve growth factors | NGF | Assumed to be deficient |
| C5a | Complement 5a | The “usual suspect” as regards the autoimmunity aspect. |
| HIF-1a | hypoxia induced factor 1 alpha |
Molecules.
| ALCAR | Acetyl-L-carnitine | Potentially helpful for cell metabolism |
| Riluzole | Counters glutamate toxicity | |
| Baicalin | Chinese skullcap | Neuroprotective agent |
| Turmeric | Neuroprotective agent | |
| Niacin | ||
| Niacinamide | Nicotinamide | |
| Niacinamide riboside | Nicotinamide riboside |
Laboratory anomalies.
Uric acid Elevated in some ALS forms
Creatine kinase
Free copper Possibly elevated
Homocysteine Elevated in some ALS forms
Neurofilaments Found in both blood and CSF of PALS.